17 KiB
| title | description | date | lastmod | slug | categories | tags | math | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南软/智软2025年开放日机试第1题 | 南京大学软件学院/智能软件与工程学院开放日机试第1题,图论+并查集问题 | 2025-07-27T11:59:00+08:00 | 2025-08-28T20:20:00+08:00 | nju01 |
|
|
true |
题目
已上传洛谷:U605360 最小交通费
有一个圆上均匀分布着L个点(编号按逆时针顺序依次为1~L)。在这些点中还存在m条弦。如果在圆弧上从一个点走到另一个相邻的点,需要支付1元的费用;但如果通过弦来走(包括交点),则无需支付费用。 例如,如图所示,如果存在弦(1,3)和(2,4),则从点1到点2可以先从1走到两条弦的交点,再从交点走到2,这样就无需收费。请你设计算法,找出某两个点之间最少的交通费。
- 程序的第一行输入三个整数:L、m、q,用空格分隔。
- 接下来输入m行,每行两个整数,表示一条弦。
- 接下来输入q行,每行两个整数,表示q个问题。如“1 2”则表示一个问题,表示点1和2之间的最少交通费。
- 程序的输出为q行,每行为一个问题的答案。
注:题中 L 最大为 3 × 10^8
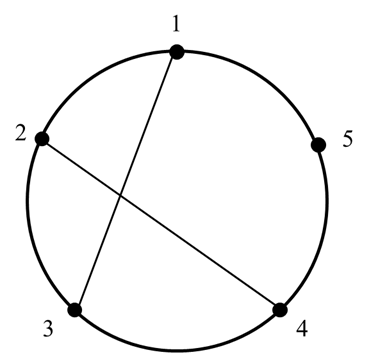
示例输入
5 2 1
1 3
2 4
1 2
示例输出
0
机试情况
南软/智软的夏令营机试是4小时4道题,每题100分,满分400分。4小时内排行榜上此题无人AC,不过有人拿到60-70分。我自己在考场也是只拿到部分分数(没想到通法,只打表了一些少数点的情况),事后思考后才成功解决。
解题思路
我们可以自然地把这个问题抽象为一个图,其中包含两种不同代价的边:
- 圆弧边:连接圆上相邻的两个点,例如点 i 和点 i+1(以及点 L 和点 1)。走这些边需要花费1元,因此它们的边权为 1。
- 免费边:所有通过弦和弦的交点构成的路径。走这些边无需花费,因此它们的边权为 0。
问题的关键在于,所有通过弦和交点能够互相到达的点,实际上构成了一个“免费交通网络”。网络内的任意两点之间都可以零费用到达。我们可以把这样一个网络视为一个连通分量。
所以我们可以用并查集 来高效地处理和合并这些连通分量。
- 初始化:将圆上的
L个点每一个都看作一个独立的集合。 - 合并弦端点:对于给定的
m条弦,每条弦(u, v)都意味着u和v是零费用连通的。我们将u和v所在的集合合并。 - 合并相交弦:接下来,我们需要找出所有相交的弦。
- 如何判断两条弦是否相交? 假设有两条弦
(a, b)和(c, d)。为了方便判断,我们先将每条弦的端点按编号从小到大排序,即u1 = min(a, b), v1 = max(a, b)和u2 = min(c, d), v2 = max(c, d)。 这两条弦在圆内相交的充要条件是,它们的端点在圆上是交错排列的。也就是说,必须满足u1 < u2 < v1 < v2或者u2 < u1 < v2 < v1。 - 对于每一对相交的弦,例如
(a, b)和(c, d),它们的所有四个端点a, b, c, d都应该在同一个零费用连通分量中。我们只需将其中任意一个点(如a)与另一条弦的任意一个点(如c)所在的集合合并即可。
- 如何判断两条弦是否相交? 假设有两条弦
完成以上步骤后,并查集就完整地记录了所有的零费用连通分量。
第二步:计算两个点之间的最短交通费
对于每一个查询 (s, t):
- 首先,我们使用并查集的
find操作检查s和t是否在同一个连通分量中。- 如果
find(s) == find(t),说明它们在同一个免费交通网络内,可以直接到达,费用为 0。
- 如果
- 如果它们不在同一个连通分量中,费用就来自于在圆弧上从一个连通分量“跳”到另一个连通分量的次数。这可以转化为一个在 “分量图” 上的最短路问题。
- 图中的每个节点代表一个连通分量。
- 如果圆弧上相邻的两个点
i和i+1属于不同的连通分量(即find(i) != find(i+1)),我们就在这两个分量对应的节点之间连一条边,权重为 1。 - 问题就变成了,在分量图上,从
s所在的分量走到t所在的分量,最少需要经过几条边。这是一个典型的无权图最短路问题,可以使用BFS 来解决。
C++ 代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric> // iota
#include <algorithm> // swap, min, max
#include <utility> // pair
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// -------- DSU 模板 --------
class DSU
{
public:
vector<int> parent;
vector<int> sz; // 按大小合并的依据 (避免与C++的size()函数重名,改为sz)
int count; // 联通分量
DSU(int n)
{
count = n;
parent.resize(n);
sz.resize(n);
iota(parent.begin(), parent.end(), 0); // 从0开始连续填充
sz.assign(n, 1);
}
int find(int i)
{
if (parent[i] == i)
return i;
return parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
}
void unite(int a, int b)
{
int root_a = find(a), root_b = find(b);
if (root_a != root_b)
{
if (sz[root_a] < sz[root_b])
std::swap(root_a, root_b);
// a是大树,b合并到a
parent[root_b] = root_a;
sz[root_a] += sz[root_b];
count--;
}
}
bool is_connected(int a, int b)
{
return find(a) == find(b);
}
// 获取联通分量
int get_count() const
{
return count;
}
// 获取i所在集合的大小
int get_size(int i)
{
return sz[find(i)];
}
};
// -------- DSU 模板结束 --------
int main()
{
// C++ 标准输入输出加速
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
int L, m, q;
cin >> L >> m >> q;
// --- 步骤 1: 预处理,构建零费用连通分量 ---
// DSU对象,大小为L+1以方便使用1-based索引
DSU dsu(L + 1);
vector<pair<int, int>> chords;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
// 存储弦,并保证端点有序,方便后续判断
chords.push_back({std::min(u, v), std::max(u, v)});
// 合并弦的两个端点
dsu.unite(u, v);
}
// 检查所有弦的配对,看它们是否相交 (O(m^2))
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < m; ++j)
{
int u1 = chords[i].first;
int v1 = chords[i].second;
int u2 = chords[j].first;
int v2 = chords[j].second;
// 判断相交:端点是否交错排列
// (u1 < u2 < v1 < v2) 或 (u2 < u1 < v2 < v1)
if ((u1 < u2 && u2 < v1 && v1 < v2) || (u2 < u1 && u1 < v2 && v2 < v1))
{
// 如果相交,合并它们所在的集合
// 只需要合并任意两个不同弦上的点即可
dsu.unite(u1, u2);
}
}
}
// --- 步骤 2: 构建“分量图” ---
// 使用 map 将 DSU 的根节点映射到从 0 开始的连续索引
map<int, int> comp_map;
int comp_idx_counter = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= L; ++i) {
int root = dsu.find(i);
if (comp_map.find(root) == comp_map.end()) {
comp_map[root] = comp_idx_counter++;
}
}
int num_components = comp_map.size();
vector<vector<int>> comp_adj(num_components);
// 遍历圆周上的所有相邻点对,构建分量图的邻接表
for (int i = 1; i <= L; ++i)
{
int p1 = i;
int p2 = (i == L) ? 1 : i + 1; // p2是p1在圆上的下一个点
// 如果相邻点属于不同分量,则在分量图上添加一条边
if (!dsu.is_connected(p1, p2))
{
int root1 = dsu.find(p1);
int root2 = dsu.find(p2);
int idx1 = comp_map[root1];
int idx2 = comp_map[root2];
comp_adj[idx1].push_back(idx2);
comp_adj[idx2].push_back(idx1);
}
}
// --- 步骤 3: 处理查询 ---
for (int i = 0; i < q; ++i)
{
int s, t;
cin >> s >> t;
// 如果起点和终点在同一个分量,费用为0
if (dsu.is_connected(s, t))
{
cout << 0 << "\n";
continue;
}
// 否则,在分量图上运行BFS
int start_comp_idx = comp_map[dsu.find(s)];
int end_comp_idx = comp_map[dsu.find(t)];
queue<pair<int, int>> bfs_q; // 存储 {当前分量索引, 距离}
vector<int> dist(num_components, -1); // -1表示未访问
bfs_q.push({start_comp_idx, 0});
dist[start_comp_idx] = 0;
while (!bfs_q.empty())
{
auto [curr_comp, d] = bfs_q.front();
bfs_q.pop();
if (curr_comp == end_comp_idx)
{
cout << d << "\n";
break;
}
for (int neighbor_comp : comp_adj[curr_comp])
{
if (dist[neighbor_comp] == -1) // 如果邻居未被访问
{
dist[neighbor_comp] = d + 1;
bfs_q.push({neighbor_comp, d + 1});
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
补充:优化思路
由于题目给出的 L 最大可达 3 * 10^8,上面代码会导致MLE。DSU dsu(L + 1) 至少需要约 2.4 GB 内存,显然是不可接受的。
解决这个问题的核心思想是离散化,也称关键点法。我们无需关心圆上所有的 L 个点,真正影响“免费交通网络”结构和连接性的,只有那些被明确提到的“关键点”。
这些“关键点”包括:
- 所有
m条弦的2*m个端点。 - 所有
q次查询的2*q个起点和终点。
除此之外的所有其他点,我们都可以看作是“空白”的弧。我们只需处理这数量级很小(最多 2m + 2q 个)的关键点,并计算它们之间的关系即可。
对原算法进行如下两个关键的改造:
- 使用基于
std::map的并查集(DSU)。 我们将 DSU 的底层实现从std::vector改为std::map。map只会为我们实际接触到的“关键点”动态分配内存,而不会预先分配一个大小为 L 的巨大数组。这直接将空间复杂度从O(L)降至O(m+q)。 - 高效构建带权的“分量图”并使用Dijkstra算法。我们不再遍历
1到L来建图,而是只关注由所有关键点分割出的关键弧。- 首先,我们将所有关键点收集起来,并进行排序和去重。
- 然后,我们遍历这个排好序的关键点列表。对于每一对在圆弧上相邻的关键点(例如列表中的
p_i和p_{i+1},以及最后一个点和第一个点形成的环形弧),它们之间就构成了一段关键弧。 - 如果这段弧两端的关键点
p_i和p_{i+1}属于不同的连通分量(即find(p_i) != find(p_{i+1})),那么这段弧就是连接两个免费区的“付费桥梁”。 - 关键修正一: 我们就在这两个分量对应的节点之间连一条边。这条边的权重并非固定的1,而是这段弧的实际长度(例如
p_{i+1} - p_i)。 - 关键修正二: 因为边的权重不同,使“分量图”成为一个带权图。因此,在求解两个分量间的最短路时,我们必须使用 Dijkstra 算法,而非原思路中的 BFS。
这样,我们就在时间和空间上都高效地解决了这个问题。算法复杂度只与 m 和 q 的大小相关,而与巨大的 L 无关。
C++ 代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <utility>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
// -------- 基于 map 的 DSU 模板 --------
class MapDSU {
public:
map<int, int> parent;
map<int, int> sz;
int find(int i) {
if (parent.find(i) == parent.end()) {
parent[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
if (parent[i] == i) {
return i;
}
return parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
}
void unite(int a, int b) {
int root_a = find(a);
int root_b = find(b);
if (root_a != root_b) {
if (sz[root_a] < sz[root_b]) {
swap(root_a, root_b);
}
parent[root_b] = root_a;
sz[root_a] += sz[root_b];
}
}
bool is_connected(int a, int b) {
// find会自动初始化不存在的点
return find(a) == find(b);
}
};
const long long INF = 1e18;
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
long long L;
int m, q;
cin >> L >> m >> q;
MapDSU dsu;
vector<pair<int, int>> chords(m);
set<int> key_points_set;
// --- 步骤1: 合并弦和相交弦 ---
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
cin >> chords[i].first >> chords[i].second;
if (chords[i].first > chords[i].second) {
swap(chords[i].first, chords[i].second);
}
dsu.unite(chords[i].first, chords[i].second);
key_points_set.insert(chords[i].first);
key_points_set.insert(chords[i].second);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < m; ++j) {
long long u1 = chords[i].first, v1 = chords[i].second;
long long u2 = chords[j].first, v2 = chords[j].second;
if (u1 > u2) {
swap(u1, u2); swap(v1, v2);
}
if (u1 < u2 && u2 < v1 && v1 < v2) {
dsu.unite(u1, u2);
}
}
}
// --- 步骤2: 收集所有关键点 ---
vector<pair<int, int>> queries(q);
for (int i = 0; i < q; ++i) {
cin >> queries[i].first >> queries[i].second;
key_points_set.insert(queries[i].first);
key_points_set.insert(queries[i].second);
}
vector<int> key_points(key_points_set.begin(), key_points_set.end());
// --- 步骤3: 构建带权的“分量图” ---
map<int, int> root_to_idx; // DSU根节点到分量图新索引的映射
int comp_idx_counter = 0;
for (int point : key_points) {
int root = dsu.find(point);
if (root_to_idx.find(root) == root_to_idx.end()) {
root_to_idx[root] = comp_idx_counter++;
}
}
int num_components = root_to_idx.size();
// 邻接表存储 {邻居分量索引, 权重}
vector<vector<pair<int, long long>>> comp_adj(num_components);
// 只需检查排序后相邻关键点之间的弧
for (size_t i = 0; i < key_points.size(); ++i) {
int p1 = key_points[i];
// p2 是 p1 在关键点列表中的下一个点(包括环形)
int p2 = key_points[(i + 1) % key_points.size()];
int root1 = dsu.find(p1);
int root2 = dsu.find(p2);
if (root1 != root2) {
long long dist;
if (i == key_points.size() - 1) { // 最后一个点到第一个点的环形距离
dist = (L - p1) + p2;
} else {
dist = p2 - p1;
}
int idx1 = root_to_idx[root1];
int idx2 = root_to_idx[root2];
comp_adj[idx1].push_back({idx2, dist});
comp_adj[idx2].push_back({idx1, dist});
}
}
// --- 步骤4: 处理查询 ---
for (const auto& query : queries) {
int s = query.first;
int t = query.second;
if (dsu.is_connected(s, t)) {
cout << 0 << "\n";
continue;
}
int start_root = dsu.find(s);
int end_root = dsu.find(t);
int start_idx = root_to_idx[start_root];
int end_idx = root_to_idx[end_root];
// Dijkstra 算法
priority_queue<pair<long long, int>, vector<pair<long long, int>>, greater<pair<long long, int>>> pq;
vector<long long> dist(num_components, INF);
dist[start_idx] = 0;
pq.push({0, start_idx});
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto [d, u] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (d > dist[u]) continue;
if (u == end_idx) break;
for (const auto& edge : comp_adj[u]) {
int v = edge.first;
long long weight = edge.second;
if (dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
pq.push({dist[v], v});
}
}
}
cout << dist[end_idx] << "\n";
}
return 0;
}